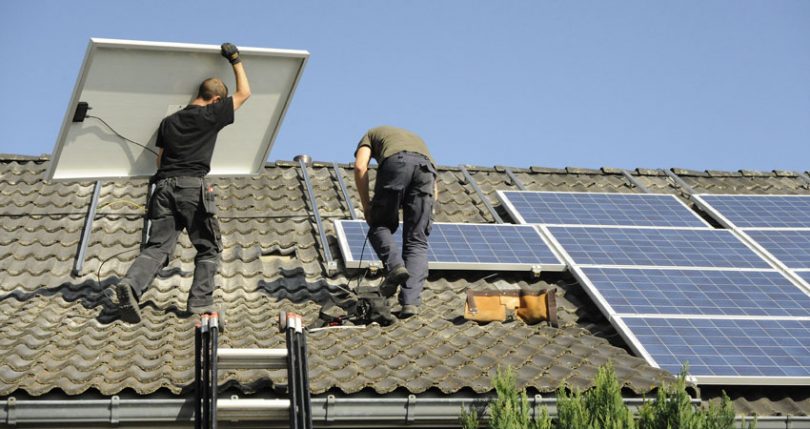
On Monday four Japanese organizations announced research plans for pricing surplus solar power and a blockchain trading system for prosumers. The organizations are the University of Tokyo, Unisys Japan, Kansai Electric Power, and Mitsubishi UFJ Bank.
Because of the widespread use of solar power, the power supply system is evolving from conventional large-scale generation to self-sustained distributed power. Kansai Electric Power has a test facility for generating electricity with solar power equipment. They’re conducting simulated transactions using blockchain involving transmitting power to multiple power consumers homes.
In the research, Unisys will develop the system, and Kansai Electric will construct the demonstration power system. The University of Tokyo will evaluate the results, and Mitsubishi UFJ Bank is providing advice on blockchains for settling transactions.
Numerous startups are exploring creating energy trading marketplaces. Power Ledger recently started a trial with Australian shopping center operator Vicinity.
Outside of startups, there’s a significant amount of activity in this area. GE, Siemens, and several others are involved in a major study with German energy agency dena. They too are exploring creating markets for alternative energies and solar in particular.
Rail company Deutsche Bahn is the largest German producer of alternative energy and has a blockchain-based platform for selling excess power to corporates.
This week the World Energy Council published a report in collaboration with PwC exploring a variety of uses cases for blockchain and energy.